| 1 |
| ||||||||||||||
| 2 |
| ||||||||||||||
| 3 |
| ||||||||||||||
| 4 |
| ||||||||||||||
| 5 |
| ||||||||||||||
| 6 |
| ||||||||||||||
| 7 |
| ||||||||||||||
| 8 |
| ||||||||||||||
| 9 |
| ||||||||||||||
| 10 |
| ||||||||||||||
| 11 |
| ||||||||||||||
| 12 |
| ||||||||||||||
| 13 |
| ||||||||||||||
| 14 |
| ||||||||||||||
| 15 |
| ||||||||||||||
| 16 |
| ||||||||||||||
| 17 |
| ||||||||||||||
| 18 |
| ||||||||||||||
| 19 |
| ||||||||||||||
| 20 |
| ||||||||||||||
| 21 |
| ||||||||||||||
| 22 |
| ||||||||||||||
| 23 |
| ||||||||||||||
3.1 CCNA 3 - Module 7
Labels: 3.1 CCNA3
Subscribe to:
Post Comments (Atom)
CCNA 1 Networking Basics (Ver. 3.1)
CCNA 2 Router & Routing Basics (Ver. 3.1)
CCNA 3 Switching Basics & Inter. (Ver. 3.1)
CCNA 4 WAN Technologies Version (Ver. 3.1)
CISCO CCNA Lectures
Lectures-1
Lectures-2
Lectures-3
Lectures-4
Lectures-5
Lectures-6
Lectures-7
Lectures-8
Lectures-9
Lectures-10
Lectures-11
Lectures-12
Lectures-13
Lectures-14
Lectures-15
Lectures-16
Lectures-17
Lectures-18
Lectures-19
Lectures-20
Lectures-21
Lectures-22
Lectures-23
Lectures-24
Lectures-25
Lectures-26
Lectures-27
Lectures-28
Lectures-29
Lectures-30
Lectures-31
Lectures-32
Lectures-33
Lectures-34
Lectures-35
Lectures-36
Lectures-37
Lectures-38
Lectures-39
Lectures-40
Lectures-41
Lectures-42
Lectures-43
Lectures-44
Lectures-45
Lectures-46
Lectures-47
Lectures-48
Lectures-49
Lectures-50
Lectures-51
Lectures-52
Lectures-53
Lectures-54
Lectures-55
Lectures-56
Lectures-57
Lectures-58
Lectures-59
Lectures-60
Lectures-2
Lectures-3
Lectures-4
Lectures-5
Lectures-6
Lectures-7
Lectures-8
Lectures-9
Lectures-10
Lectures-11
Lectures-12
Lectures-13
Lectures-14
Lectures-15
Lectures-16
Lectures-17
Lectures-18
Lectures-19
Lectures-20
Lectures-21
Lectures-22
Lectures-23
Lectures-24
Lectures-25
Lectures-26
Lectures-27
Lectures-28
Lectures-29
Lectures-30
Lectures-31
Lectures-32
Lectures-33
Lectures-34
Lectures-35
Lectures-36
Lectures-37
Lectures-38
Lectures-39
Lectures-40
Lectures-41
Lectures-42
Lectures-43
Lectures-44
Lectures-45
Lectures-46
Lectures-47
Lectures-48
Lectures-49
Lectures-50
Lectures-51
Lectures-52
Lectures-53
Lectures-54
Lectures-55
Lectures-56
Lectures-57
Lectures-58
Lectures-59
Lectures-60
CISCO CCNA Tutorials
ACCESS ONLINE
INDEX
PRESENTATION
DOWNLOADS
ANSWERS
DOWNLOADS
ANSWERS
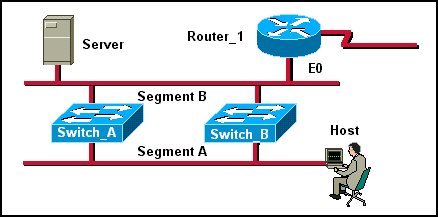
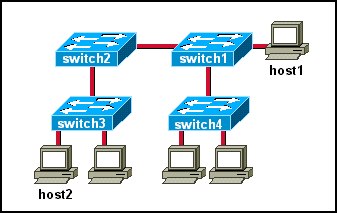
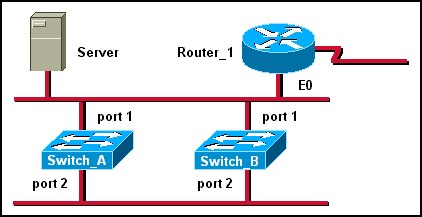








0 comments:
Post a Comment